Mono-n-butyltin trichloride
Agent Name
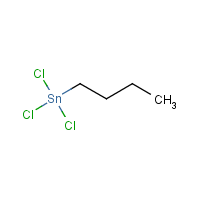
Mono-n-butyltin trichloride
CAS Number
1118-46-3
Formula
C4-H9-Cl3-Sn
Major Category
Metals
Synonyms
Butylstannium trichloride; Butyltin trichloride; Butyltrichlorostannane; Butyltrichlorotin; Chlorid n-butylcinicity [Czech]; Monobutyltin trichloride; Monotributyltin trichloride; n-Butyltin trichloride; Stannane, butyltrichloro-; Stannane, trichlorobutyl-; Tin, n-butyl-, trichloride; Trichlorobutylstannane; Trichlorobutyltin; [ChemIDplus]
Category
Tin Compounds, Organic
Description
Colorless liquid; [HSDB] Yellow to red clear liquid; [MSDSonline]
Sources/Uses
A degradation product of dibutyltin and tributyltin (antifouling agents in marine paints); Used as an intermediate for other mono-n-butyltin compounds, a PVC stabilizer, and a hot-end coating of glass bottles; [HSDB]
Comments
A strong skin irritant Oral LD50 (rat) = 2140 mg/kg; [Sax] Corrosive to skin and eyes; [eChemPortal: ERMA] A corrosive substance that can cause injury to the skin, eyes, and respiratory tract; Inhalation may cause chemical pneumonitis and pulmonary edema; [MSDSonline] See "Tin, organic compounds."
Biomedical References
Exposure Assessment
Skin Designation (ACGIH)
Yes
TLV (ACGIH)
0.1 mg/m3, as Sn
STEL (ACGIH)
0.2 mg/m3, as Sn
PEL (OSHA)
0.1 mg/m3, as Sn
MAK
0.02 mg/m3, inhalable fraction, as Sn
IDLH (NIOSH)
25 mg/m3, as Sn
Explanatory Notes
Organic tin compounds have a "skin" designation and are classified as "A4" (Not classifiable as human carcinogen); [ACGIH]
Adverse Effects
Toxic Pneumonitis
Yes
Neurotoxin
Other CNS neurotoxin
Hepatotoxin
Hepatoxic (a) from occupational exposure (secondary effect) or (b) in animal studies or in humans after ingestion
Dermatotoxin
Skin burns
ACGIH Carcinogen
Not Classifiable
Diseases, Processes, and Activities Linked to This Agent
Processes
Industrial Processes with risk of exposure: