Triethylene glycol monomethyl ether
Agent Name
Triethylene glycol monomethyl ether
Alternative Name
TEGME
CAS Number
112-35-6
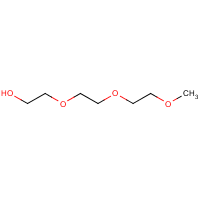
Formula
C7-H16-O4
Major Category
Solvents
Synonyms
2-(2-(2-Methoxyethoxy)ethoxy)ethanol; 3,6,9-Trioxa-1-decanol; Dowanol TMAT; Ethanol, 2-(2-(2-methoxyethoxy)ethoxy)-; Methoxytriethylene glycol; Methoxytriglycol; Methyl triethylene glycol; Methyltrioxitol; Poly-Solv TM; Triethylene glycol methyl ether; Triethylene glycolmonomethyl ether; Triglycol monomethyl ether; [ChemIDplus] TGME; [eChemPortal: SIDSUNEP]
Category
Glycol Ethers (E Series)
Description
Colorless liquid; [HSDB] Odorless; [CAMEO]
Sources/Uses
Used as coupling solvent (water-based paints), for blending brake and hydraulic fluids, and as a plasticizer and wetting agent (resins and paints); [HSDB] Used as raw material for automotive hydraulic brake fluids and a solvent in coatings, printing inks, cleaning products, cutting oils, and deicing agents; [eChemPortal: SIDSUNEP]
Comments
In lethal-dose animal studies, causes liver injury; Oral doses of 4000 mg/kg/day for 91 days cause testicular injury in rats; Developmental toxicity is seen in rats receiving >1000 mg/kg/day; Genotoxic studies were negative; [OECD SIDS: 2-(2-(2-Methoxyethoxy)ethoxy)ethanol - 1996] No listed effects of short-term or long-term exposure; [ICSC] May form unstable peroxides in the presence of oxygen; [CAMEO] May cause mild skin and eye irritation; [eChemPortal: SIDSUNEP] See "GLYCOL ETHERS."
Biomedical References
Exposure Assessment
MAK
50 mg/m3. inhalable fraction
Vapor Pressure
0.0035 mm Hg
Explanatory Notes
VP from ChemIDplus;
NFPA
must be preheated
Adverse Effects
Neurotoxin
Acute solvent syndrome
Hepatotoxin
Hepatoxic (a) from occupational exposure (secondary effect) or (b) in animal studies or in humans after ingestion
Diseases, Processes, and Activities Linked to This Agent
Diseases
Occupational diseases associated with exposure to this agent:
Processes
Industrial Processes with risk of exposure: