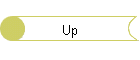The main form for displaying chemical information is the Agents form with five tabs. The first three pages of that form are shown below. Styrene has a hazard score of 13 = 11 (effects) + 2 (processes). The "Comments" box documents references for adverse effects. The user can click the "Print Agent" button to print two pages showing the information in the first four tabs of the form. The "Hyperlink" is a link to other information on the web.
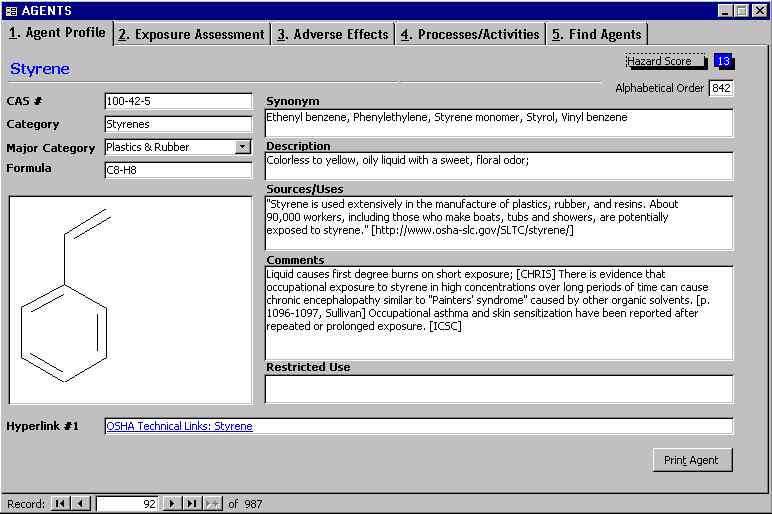
The second page of the tabbed Agents form is the Exposure Assessment page. The information on this page was selected to help the clinician estimate the dose received by the exposed worker. Recommended maximum air concentrations in ppm are shown for TLV, STEL and Ceiling (ACGIH); PEL (OSHA); MAK (Federal Republic of Germany); and IDLH (Immediately Dangerous to Life or Health from NIOSH). The user can click the toggle button to convert to mg/m3 values and click it again to convert back to ppm.
Vapor pressure X 1300 is an estimate of the saturated concentration of the chemical after a spill in a confined space at room temperature. (See "Solvent Vapor Pressure and Health Hazards" in Sullivan, p. 1086-7.) For example, a chemical with a VP of 380 mmHg would be expected to reach a concentration of 0.5 million ppm, and one with a VP of 760 mmHg could reach a concentration of a million ppm (760 X 1300 = 1,000,000). Styrene has the potential to reach a concentration of 6500 ppm after a spill in a confined space. This concentration is higher than both the IDLH and the LC50.
The IDLH is the maximum concentration from which, in the event of respirator failure, one could escape within 30 minutes without experiencing any escape-impairing or irreversible health effects. The LC50 is the 30-minute exposure concentration at which half of the experimental animals are likely to die (from lack of oxygen to the brain induced by anesthesia for the case of styrene). The RD50, an estimate of severe respiratory irritation, is the 10-minute exposure concentration producing a 50% respiratory rate reduction in mice or rats. The NFPA flammability code of 3 indicates that styrene may ignite at ambient temperature. See Chemical Hazard Scores for an explanation of "Exposure Points" and "TIH."
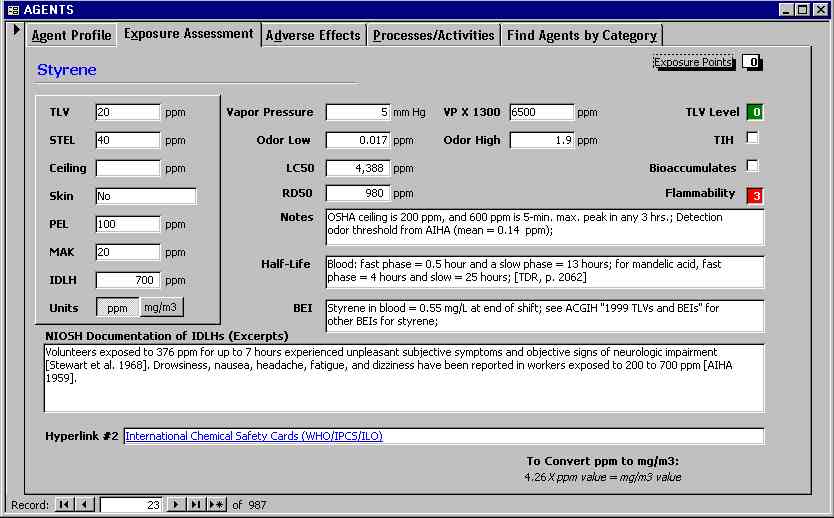
The third page presents the potential adverse effects of styrene exposure. Like other solvents, styrene can disrupt brain function causing fatigue and lightheadedness at lower doses and inebriation and anesthesia at higher doses. ACD is an abbreviation for allergic contact dermatitis, while PACD and PICD stand for photoallergic and photoirritant contact dermatitis. An "Uncoupler" is a chemical like pentachlorophenol that can cause a hypermetabolic state by poisoning cellular respiration (uncoupling oxidative phosphorylation). A Hematotoxin is a chemical that can cause methemoglobinemia, aplastic anemia or hemolytic anemia.
Revised: May 30, 2018