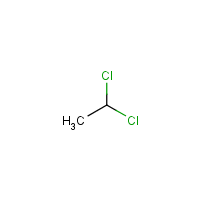
1,1-Dichloroethane
Agent Name
1,1-Dichloroethane
Alternative Name
Ethylidene chloride
CAS Number
75-34-3
Formula
C2-H4-Cl2
Major Category
Solvents
Synonyms
Asymmetrical dichloroethane; 1,1-Dichlorethane; 1,1-Ethylidene dichloride; Chlorinated hydrochloric ether; Ethane, 1,1-dichloro-; Ethylidene chloride; Ethylidene dichloride; alpha,alpha-Dichloroethane; 1,1-Dichloorethaan [Dutch]; 1,1-Dichloraethan [German]; 1,1-Dicloroetano [Italian]; Aethylidenchlorid [German]; Chlorure d'ethylidene [French]; Cloruro di etilidene [Italian]; [ChemIDplus] Dichloromethylmethane; [Merck Index] Dichloroethane, 1,1-; 1,1-Ethylene dichloride; HCC 150A; [CAMEO] UN2362
Category
Chlorinated Aliphatics
Description
Colorless, oily liquid with a chloroform-like odor; [NIOSH] Clear colorless to light yellow liquid; [Acros Organics MSDS]
Sources/Uses
Used as a chemical intermediate, grain fumigant, and solvent for plastics and oils; in the past, used as an anesthetic; [ACGIH] Used as a cleaning agent, in metal degreasing, rubber cementing, in fabric spreading, ore flotation, fire extinguishing, as an insecticide spray, extraction solvent, coupling agent in antiknock gasoline, paint, varnish, and finish remover, and to make high vacuum rubber; [HSDB] Used as a reagent and solvent for paint and varnishes; [Merck Index]
Comments
1,1-Dichoroethane is less toxic to the liver than other chlorinated solvents. [ACGIH] The halogenated solvents are CNS depressants; A 14 year old boy developed fatal hepatorenal syndrome after ingesting about 50 ml of dichloroethane; [Sullivan, p. 739-40] May have CNS effects, causing unconsciousness at high exposure levels; May cause liver and kidney injury; [ICSC] An eye and respiratory tract irritant; Prolonged or repeated exposure can cause skin burns; Inhalation may cause CNS depression; May cause liver and kidney injury; [HSDB] An eye and respiratory tract irritant; Harmful by ingestion; [Acros Organics MSDS]
Biomedical References
Exposure Assessment
Skin Designation (ACGIH)
Insufficient data
TLV (ACGIH)
100 ppm
PEL (OSHA)
100 ppm
MAK
51.88 ppm
IDLH (NIOSH)
3000 ppm
Excerpts from Documentation for IDLHs
Patty [1963] reported that rats survived 8hour exposures to 4,000 ppm, but died at 16,000 ppm [Smyth 1956].
Vapor Pressure
227 mm Hg
Odor Threshold Low
49 ppm
Odor Threshold High
1359 ppm
Lethal Concentration
LC50 (rat) = 13,000 ppm/4hr
Explanatory Notes
Odor threshold from AIHA; Flash point = -17 deg C; VP from HSDB;
Half Life
Based on information from its use as an anesthetic in the past: completely removed within 2 days; [TDR, p. 490]
Reference Link #2
NFPA
may ignite at ambient temp
Adverse Effects
Neurotoxin
Acute solvent syndrome
Hepatotoxin
Hepatoxic (a) from occupational exposure (secondary effect) or (b) in animal studies or in humans after ingestion
Nephrotoxin
Yes
ACGIH Carcinogen
Not Classifiable
Diseases, Processes, and Activities Linked to This Agent
Diseases
Occupational diseases associated with exposure to this agent:
Processes
Industrial Processes with risk of exposure: