Boric acid
Agent Name
Boric acid
CAS Number
10043-35-3
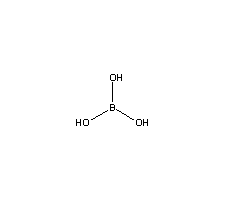
Formula
B-H3-O3
Major Category
Metals
Synonyms
Basilit B; Boracic acid; Boric acid (VAN); Borofax; Boron hydroxide; Boron trihydroxide; Borsaeure; Borsaure [German]; Dr.'s 1 Flea Terminator DF; Dr.'s 1 Flea Terminator DFPBO; Dr.'s 1 Flea Terminator DT; Dr.'s 1 Flea Terminator DTPBO; Flea Prufe; Orthoboric acid; Orthoboric acid (B(OH)3); Orthoborsaeure; Super Flea Eliminator; Three elephant; Trihydroxyborone; component of Aci-Jel; [ChemIDplus]
Category
Metalloid Compounds (Boron)
Description
Colorless crystals or white powder or granules; odorless; [Merck Index] White odorless powder; [Alfa Aesar MSDS]
Sources/Uses
Used as an insecticide to kill ants and roaches, as a soldering flux, a flame retardant and weatherproofing agent; also used as an additive to dyes, nickeling baths, film developers, glass, enamels, soaps, paints, paper, adhesives, and steel; [HSDB] Used as a flux, an additive for heat-resistant borosilcate glass and glass fibers, a flame retardant for textile and insulation products, a fungicide for citrus fruits, an eye medicine, and a solute for nickel electroplating baths; Boric acid is formed by crystallizing a solution of hydrochloric acid or sulfuric acid and borax. [Hawley] Used for weatherproofing wood, as a preservative, in cosmetics, printing and dyeing, electric condensers, photography, and painting, for impregnating wicks and hardening steel, and to make cements, crockery, porcelain, borates, leather, carpets, hats, and artificial gems; Used therapeutically as an astringent and antiseptic and as a veterinary antibacterial and antifungal; [Merck Index] Registered US pesticide uses include insecticides (stomach poisons for ants, cockroaches, silverfish, and termites), fungicides (wood preservatives), and herbicides (desiccants, photosynthesis interrupters, and algae control in swimming pools and sewage systems); [Reference #1]
Comments
In typical cases of poisoning by ingestion, the victims have vomiting and diarrhea, skin desquamation, mucosal erosions, and injury to the liver and kidneys; Evidence of neurotoxicity includes seizures, delirium, and coma. The mechanism of toxicity is not known. [Ford, p. 750-1] A skin irritant; [Quick CPC] In high-dose reproductive studies of animals, boric acid causes testicular damage and fetal loss. [Frazier, p. 252-4] The basis for the TLV for inorganic borate compounds (including boric acid) is irritation of the nose and respiratory tract. Studies of workers exposed to sodium borate dusts found no evidence of pulmonary function or reproductive impairment. [ACGIH] A skin, eye, and respiratory tract irritant; May have effects on the GI tract, liver, and kidneys; Can be absorbed through skin; May cause adverse effects to human reproduction, based on animal studies; [ICSC] Not likely to pose a hazard to human reproduction, based on usual human exposures being well below the doses considered to have adverse effects on reproduction; [REPROTOX] A mild skin irritant; May cause reproductive effects; [Alfa Aesar MSDS] See "Boron."
Reference Link #1
Biomedical References
Exposure Assessment
Skin Designation (ACGIH)
Insufficient data
TLV (ACGIH)
2 mg/m3, inhalable fraction
STEL (ACGIH)
6 mg/m3, inhalable fraction
MAK
10 mg/m3, inhalable fraction
Lethal Concentration
LCLo (rat) = 28 mg/m3/4hr
Explanatory Notes
Melting point = 171 deg C; TLV is for "Borate compounds, inorganic" for "all forms of sodium borate and boric acid." [ACGIH] LC50 (rat) > 160 mg/m3; [Reference #1]
Adverse Effects
Neurotoxin
Other CNS neurotoxin
Hepatotoxin
Hepatoxic (a) from occupational exposure (secondary effect) or (b) in animal studies or in humans after ingestion
Reproductive Toxin
Yes
ACGIH Carcinogen
Not Classifiable
Diseases, Processes, and Activities Linked to This Agent
Processes
Industrial Processes with risk of exposure:
- Applying Wood Preservatives
- Brazing
- Cement Producing
- Electroplating
- Farming (Pesticides)
- Glass Manufacturing
- Leather Tanning and Processing
- Painting (Pigments, Binders, and Biocides)
- Photographic Processing
- Sewer and Wastewater Treatment
- Steel Producing
- Textiles (Fiber & Fabric Manufacturing)
- Textiles (Printing, Dyeing, or Finishing)
- Using Disinfectants or Biocides
- Welding