Lead(II) sulfate
Agent Name
Lead(II) sulfate
CAS Number
7446-14-2
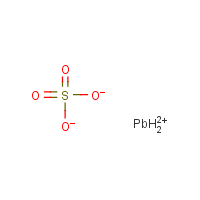
Formula
H2-O4-S.Pb
Major Category
Metals
Synonyms
Anglislite; Bleisulfat [German]; C.I. 77630; C.I. Pigment White 3; CI 77630; CI pigment white 3; Fast White; Freemans White Lead; HB 2000; Lead Bottoms; Lead monosulfate; Lead sulfate; Lead(II) Sulfate (1:1); Milk White; Mulhouse White; Natural anglesite; Pigment White 3; Sulfate de plomb [French]; Sulfuric acid, lead(2+) salt (1:1); TS 100 (sulfate); [ChemIDplus] UN1794 (Lead sulfate, with more than 3% free acid)
Category
Lead Compounds, Inorganic
Description
White powder that is insoluble in water; [CAMEO]
Sources/Uses
Used to stabilize clay soils, and to weight fabrics; Also used in galvanic batteries and rapidly drying varnishes; Has been used in lithography and with silver bromide in photography; [HSDB] Used in storage batteries and paint (pigment); [Hawley] Workers are exposed in mines and smelters and during production of lead storage batteries; [HSDB]
Comments
A strong irritant; [Hawley] Corrosive to skin and eyes; Toxic by ingestion; [Sax] See "Lead" and linked occupational diseases.
Biomedical References
Exposure Assessment
BEI
Lead in blood = 200 ug/L (20 ug/100 ml); sampling time not critical; [ACGIH]
TLV (ACGIH)
0.05 mg/m3, as Pb
PEL (OSHA)
0.05 mg/m3, as Pb
Explanatory Notes
mp = 2138 deg F; [CAMEO] The Guide in the Emergency Response Guidebook is for "Lead sulfate, with more than 3% free acid."
Adverse Effects
Neurotoxin
Predominantly motor
Hepatotoxin
Hepatoxic (a) from occupational exposure (secondary effect) or (b) in animal studies or in humans after ingestion
Nephrotoxin
Yes
Reproductive Toxin
Yes
Dermatotoxin
Skin burns
IARC Carcinogen
Probable (2a)
NTP Carcinogen
Anticipated human carcinogen
ACGIH Carcinogen
Confirmed Animal
Diseases, Processes, and Activities Linked to This Agent
Diseases
Occupational diseases associated with exposure to this agent:
Processes
Industrial Processes with risk of exposure: