sec-Amyl acetate
Agent Name
sec-Amyl acetate
Alternative Name
2-Pentyl acetate
CAS Number
626-38-0
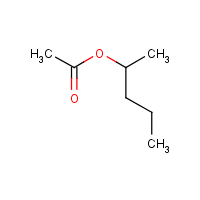
Formula
C7-H14-O2
Major Category
Solvents
Synonyms
1-Methylbutyl acetate; 2-Acetoxypentane; 2-Amylester kyseliny octove [Czech]; 2-Pentanol, acetate; 2-Pentyl acetate; sec-Amyl acetate; sek.Amylester kyseliny octove [Czech]; [ChemIDplus]
Category
Esters (<C12)
Description
Colorless liquid with a mild odor; [NIOSH]
Sources/Uses
Used as a solvent for ethyl cellulose, nitrocellulose, printing inks; also used in the production of coatings and cements; [ACGIH]
Comments
Esters may induce narcosis in animals, but workers' exposures are limited by irritating effects. See appendix in: [Dick RB, et al. Chemicals in the workplace: incorporating human neurobehavioral testing into the regulatory process. Am J Ind Med. 1998 May;33(5):439-53.] The pentyl acetates are sensory irritants in the work environment. At higher levels in animal experiments, they cause narcosis, hepatotoxicity, and developmental toxicity. [ACGIH]
Biomedical References
Exposure Assessment
Skin Designation (ACGIH)
Insufficient data
TLV (ACGIH)
50 ppm
STEL (ACGIH)
100 ppm
PEL (OSHA)
125 ppm
MAK
50 ppm
IDLH (NIOSH)
1000 ppm
Excerpts from Documentation for IDLHs
The chosen IDLH is based on the statement by Browning [1965] that exposure to 4,000 ppm of a mixture of n-amyl acetate and isoamyl acetate produced complete loss of reflexes in rabbits within an hour [Koelsch 1912], and on the statement by Sax [1975] that 5,000 ppm n-amyl acetate produced deep narcosis in cats in 30 minutes.
Vapor Pressure
9.78 mm Hg
Odor Threshold Low
0.002 ppm
Odor Threshold High
0.08 ppm
Explanatory Notes
Odor threshold from CHEMINFO; Flash point = 32 deg C; VP = 7 mm Hg @ 20 deg C; [HSDB]
Half Life
No reports found; [TDR, p. 95]
NFPA
may ignite at ambient temp
Adverse Effects
Neurotoxin
Acute solvent syndrome
Hepatotoxin
Hepatoxic (a) from occupational exposure (secondary effect) or (b) in animal studies or in humans after ingestion
Diseases, Processes, and Activities Linked to This Agent
Diseases
Occupational diseases associated with exposure to this agent:
Processes
Industrial Processes with risk of exposure: