Carbon dioxide
Agent Name
Carbon dioxide
CAS Number
124-38-9
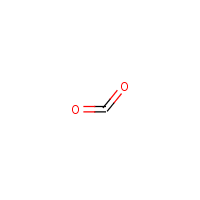
Formula
C-O2
Major Category
Toxic Gases & Vapors
Synonyms
AER Fixus; After-damp; Anhydride carbonique [French]; Carbon dioxide; Carbon oxide; Carbon oxide, di-; Carbonic acid anhydride; Carbonic acid gas; Carbonic anhydride; Carbonica; Dioxido de carbono [Spanish]; Dioxyde de carbone [French]; Dry ice; Khladon 744; Kohlendioxyd [German]; Kohlensaure [German]; R 744; [ChemIDplus] UN1013; UN1845; UN2187
Category
Simple Asphyxiants
Description
Colorless, odorless gas; Note: Shipped as a liquefied compressed gas. Solid form is utilized as dry ice; [NIOSH]
Sources/Uses
Used in carbonated beverages, fire extinguishers, dry ice, and propellants; A product of fermentation; [ACGIH] A product of animal metabolism and released when organic materials burn; a constituent of the earth's atmosphere at about 0.03% by volume; [Merck Index # 1809] Used in the deliming stage of leather production; [PMID 21938525]
Comments
Possible frostbite from contact with liquid; [NIOSH] Simple asphyxiant; [ICSC]
Biomedical References
Exposure Assessment
Skin Designation (ACGIH)
Insufficient data
TLV (ACGIH)
5000 ppm
STEL (ACGIH)
30000 ppm
PEL (OSHA)
5000 ppm
MAK
5000 ppm
IDLH (NIOSH)
40000 ppm
Excerpts from Documentation for IDLHs
Other human data: Signs of intoxication have been produced by a 30minute exposure at 50,000 ppm [Aero 1953], and a few minutes exposure at 70,000 to 100,000 ppm produces unconsciousness [Flury and Zernik 1931]. It has been reported that submarine personnel exposed continuously at 30,000 ppm were only slightly affected, provided the oxygen content of the air was maintained at normal concentrations [Schaefer 1951]. It has been reported that 100,000 ppm is the atmospheric concentration immediately dangerous to life [AIHA 1971] and that exposure to 100,000 ppm for only a few minutes can cause loss of consciousness [Hunter 1975].
Adverse Effects
Other Poison
Simple Asphyxiant
Diseases, Processes, and Activities Linked to This Agent
Diseases
Occupational diseases associated with exposure to this agent:
Processes
Industrial Processes with risk of exposure:
Activities
Activities with risk of exposure: