Ethylene dichloride
Agent Name
Ethylene dichloride
Alternative Name
1,2-Dichloroethane
CAS Number
107-06-2
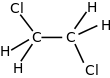
Formula
C2-H4-Cl2
Major Category
Solvents
Synonyms
Ethylene chloride; Glycol dichloride; 1,2-Dichloroethane; [NIOSH]
Category
Chlorinated Aliphatics
Description
Colorless liquid with a pleasant, chloroform-like odor. [Note: Decomposes slowly, becomes acidic & darkens in color.] [NIOSH]
Sources/Uses
Used in organic synthesis; used in the past as a solvent, degreaser, paint remover, and fumigant; [ACGIH] Has been used as a dry cleaning agent and solvent for degreasing, resins, adhesives, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals; [HSDB]
Comments
Liquid causes first degree burns on short exposure; [CHRIS] Can cause nausea and vomiting, narcosis, liver and kidney injury, and death after high inhalation exposure; [ACGIH]
Restricted
Use as fumigant suspended by EPA due to toxicity. [Sullivan, p. 1053]
Reference Link #1
Biomedical References
Exposure Assessment
Skin Designation (ACGIH)
Insufficient data
TLV (ACGIH)
10 ppm
PEL (OSHA)
50 ppm, Ceiling(OSHA) = 100 ppm (200 ppm for 5-min peak in any 3 hrs)
IDLH (NIOSH)
50 ppm
Excerpts from Documentation for IDLHs
The chosen IDLH is based on the maximum timeconcentration in air of 1,000 ppm which was survived by female rats for 1.5 hours.
Vapor Pressure
78.9 mm Hg
Odor Threshold Low
6 ppm
Odor Threshold High
111 ppm
Lethal Concentration
LC50 (rat) = 1,000 ppm/7 hr
Explanatory Notes
Detection odor threshold from AIHA (mean = 26 ppm); VP from HSDB;
Half Life
Whole body (animal studies): complete elimination within 48 hours; [TDR, p. 649]
Reference Link #2
NFPA
may ignite at ambient temp
ERPG-1
50 ppm
ERPG-2
200 ppm
ERPG-3
300 ppm
Adverse Effects
Neurotoxin
Acute solvent syndrome
Hepatotoxin
Occupational hepatotoxin (principal effect)
Nephrotoxin
Yes
Dermatotoxin
Skin burns
IARC Carcinogen
Possible (2b)
NTP Carcinogen
Anticipated human carcinogen
ACGIH Carcinogen
Not Classifiable
Diseases, Processes, and Activities Linked to This Agent
Diseases
Occupational diseases associated with exposure to this agent:
Processes
Industrial Processes with risk of exposure: