Hydrazine sulfate
Agent Name
Hydrazine sulfate
CAS Number
10034-93-2
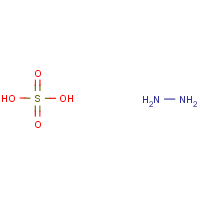
Formula
H4-N2.H2-O4-S
Major Category
Nitrogen Compounds
Synonyms
Diamidogen sulfate; Diamine sulfate; HS; Hydrazine dihydrogen sulfate salt; Hydrazine hydrogen sulfate; Hydrazine monosulfate; Hydrazine sulfate (1:1); Hydrazine sulfate (VAN); Hydrazine sulphate; Hydrazine, sulfate (1:1); Hydrazinium sulfate; Hydrazinium(2+) sulfate; Hydrazonium sulfate; Idrazina solfato [Italian]; Segidrin; Sehydrin; Siran hydrazinu [Czech]; [ChemIDplus]
Category
Hydrazines
Description
White solid; [Hawley]
Sources/Uses
Used in the gravimetric estimation of nickel, cobalt, and cadmium; in the refining of rare metals; in separating polonium from tellurium; for determination of arsenic in metals; in condensation reactions; and to make hydrazine hydrate and other chemicals; Also used as an antioxidant in soldering flux for light metals, a reducing agent in the analysis of minerals and slags, a catalyst in making acetate fibers, and a germicide to destroy fungi and molds; [HSDB]
Comments
Emergency treatment: "Hydrazines"; Hydrazines can cause severe eye damage. They can cause seizures, liver injury, hemolysis, and delayed pulmonary edema. [HSDB] A strong reducing agent; May cause irritation; [CAMEO] An irritant; May cause skin sensitization; May be fatal by inhalation; [MSDSonline] See "Hydrazine."
Biomedical References
Adverse Effects
Skin Sensitizer
Yes
Methemoglobinemia
MetHgb is secondary toxic effect
Neurotoxin
Other CNS neurotoxin
Hepatotoxin
Hepatoxic (a) from occupational exposure (secondary effect) or (b) in animal studies or in humans after ingestion
NTP Carcinogen
Anticipated human carcinogen
Diseases, Processes, and Activities Linked to This Agent
Diseases
Occupational diseases associated with exposure to this agent:
Processes
Industrial Processes with risk of exposure: