Nitromethane
Agent Name
Nitromethane
CAS Number
75-52-5
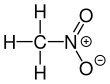
Formula
C-H3-N-O2
Major Category
Nitrogen Compounds
Synonyms
Nitrocarbol; [NIOSH]
Category
Nitros, Aliphatic
Description
Colorless, oily liquid with a disagreeable odor; [NIOSH]
Sources/Uses
Used as a stabilizer of halogenated organic solvents, a rocket and racing fuel, an explosive, and a chemical intermediate; [ACGIH] Also used as a solvent for cyanoacrylate adhesives, polymers, and waxes; [CHEMINFO]
Comments
The lethal oral dose in humans is between 0.5 and 5 g/kg. Nitromethane can cause respiratory irritation, narcosis, and possibly liver injury. Animals in subchronic inhalation studies suffer thyroid injury. [ACGIH] Not irritating to the skin; Can detonate under conditions of normal temperature and pressure; [CHEMINFO] A skin, eye, and respiratory tract irritant; May cause CNS depression; May cause effects on the liver, kidneys, and peripheral nervous system after repeated exposures; "Will turn shock-sensitive if contaminated with acids, bases, metal oxides, hydrocarbons and other combustible materials." [ICSC]
Reference Link #1
Biomedical References
Exposure Assessment
Skin Designation (ACGIH)
Insufficient data
TLV (ACGIH)
20 ppm
PEL (OSHA)
100 ppm
IDLH (NIOSH)
750 ppm
Excerpts from Documentation for IDLHs
Basis for original (SCP) IDLH: The chosen IDLH is based on the statement by Browning [1965] that with concentrations above 1,000 ppm, if the product of this and the time of exposure was greater than 1000 (e.g., 1,000 ppm for 3 hours) some of the animals, including 1 monkey, died. Also, AIHA [1961] reported severe eye irritation at 500 ppm [Machle et al. 1940]. . . . Human data: None relevant for use in determining the revised IDLH.
Vapor Pressure
35.8 mm Hg
Odor Threshold Low
3.5 ppm
Odor Threshold High
100 ppm
Lethal Concentration
LCLo (rat) = 12,750 mg/m3/1H
Explanatory Notes
Odor threshold from CHEMINFO; Flash point = 95-96 deg F; [CHEMINFO] VP from HSDB;
NFPA
may ignite at ambient temp
Adverse Effects
Neurotoxin
Sensorimotor
Hepatotoxin
Hepatoxic (a) from occupational exposure (secondary effect) or (b) in animal studies or in humans after ingestion
IARC Carcinogen
Possible (2b)
NTP Carcinogen
Anticipated human carcinogen
ACGIH Carcinogen
Confirmed Animal
Diseases, Processes, and Activities Linked to This Agent
Diseases
Occupational diseases associated with exposure to this agent:
Processes
Industrial Processes with risk of exposure: