Resorcinol
Agent Name
Resorcinol
CAS Number
108-46-3
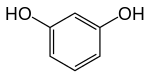
Formula
C6-H6-O2
Major Category
Other Classes
Synonyms
1,3-Benzenediol; 1,3-Dihydroxybenzene; 3-Hydroxycyclohexadien-1-one; 3-Hydroxyphenol; Benzene, 1,3-dihydroxy-; Benzene, m-dihydroxy-; C.I. 76505; C.I. Developer 4; C.I. Oxidation Base 31; Developer O; Developer R; Developer RS; Dihydroxybenzol; Durafur developer G; Fouramine RS; Fourrine 79; Fourrine EW; Nako TGG; Pelagol Grey RS; Pelagol RS; Phenol, m-hydroxy-; Resorcin; Resorcine; Resorcinol; Resorcinolum; Resorzin; m-Benzenediol; m-Dihydroxybenzene; m-Dioxybenzene; m-Hydroquinone; m-Hydroxyphenol; [ChemIDplus] UN2876
Category
Phenols
Description
White needles, plates, crystals, flakes, or powder with a faint odor. [Note: Turns pink on exposure to air or light, or contact with iron.]; [NIOSH]
Sources/Uses
Used in tanning, photography, tire building, and in the manufacturing of resorcinol-formaldehyde resins; also used in dyes, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, skin creams, laminates, and adhesives; [ACGIH]
Comments
Resorcinol may cause methemoglobinemia after ingestion of large amounts. Rats develop increased liver weights in subchronic feeding studies. [ACGIH] Allergic contact dermatitis reported in hairdressers; [Kanerva, p. 1833] Very irritating to the eyes and skin--may cause redness and pain; Can induce methemoglobinemia; [ICSC] Danger of skin sensitization; [MAK]
Reference Link #1
Biomedical References
Exposure Assessment
Skin Designation (ACGIH)
Insufficient data
TLV (ACGIH)
10 ppm
STEL (ACGIH)
20 ppm
Vapor Pressure
0.000489 mm Hg
Lethal Concentration
LCLo (rat) = 160 mg/m3/1h
Explanatory Notes
Flash point = 261 deg F; VP from HSDB;
NFPA
must be preheated
Adverse Effects
Skin Sensitizer
Yes
Methemoglobinemia
MetHgb is secondary toxic effect
Hepatotoxin
Hepatoxic (a) from occupational exposure (secondary effect) or (b) in animal studies or in humans after ingestion
Dermatotoxin
Skin burns
IARC Carcinogen
Not classifiable
ACGIH Carcinogen
Not Classifiable
Diseases, Processes, and Activities Linked to This Agent
Diseases
Occupational diseases associated with exposure to this agent:
Processes
Industrial Processes with risk of exposure: