Copper(II) oxide
Agent Name
Copper(II) oxide
Alternative Name
Cupric oxide
CAS Number
1317-38-0
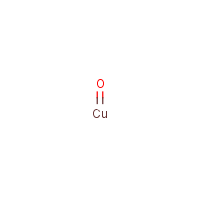
Formula
Cu-O
Major Category
Metals
Synonyms
Cupric oxide; Banacobru OL; Black copper oxide; Boliden Salt K-33; Boliden-CCA Wood Preservative; C.I. 77403; C.I. Pigment Black 15; CCA Type C Wood Preservative; CI 77403; CI Pigment black 15; Chrome Brown; Copacaps; Copper Brown; Copper monooxide; Copper monoxide; Copper oxide; Copper(2+) oxide; Copporal; Farboil Super Tropical Anti-Fouling 1260; Natural tenorite; Osmose K-33 Wood Preservative; Osmose K-33-A Wood Preservative; Osmose K-33-C Wood Preservative; Osmose P-50 Wood Preservative; Paramelaconite; Wolmanac concentrate; [ChemIDplus] UN3077
Category
Metals, Inorganic Compounds
Description
Steel-grey to black solid; [Merck Index] Black odorless powder; [Alfa Aesar MSDS]
Sources/Uses
Used as a pigment (glass, ceramics, enamels, glazes, and artificial gems), flux (copper metallurgy, glass fibers, and bronze welding), polishing agent for optical glass, pesticide (antifouling paints, wood preservative, and potato plant and seedling insecticide), solvent for chromic iron ores, and reagent in analytical chemistry; Also used to make rayon, other copper compounds, acrylates, batteries, electrodes, and magnetic storage devices, for desulfurizing oils, in sweetening petroleum gases, electroplating, purification of hydrogen and waste gases, pyrotechnics, phosphor exciters, catalysts, cloud seeding agents, solar energy devices, cigarette additives, animal feeds, and catalytic converters; [HSDB] Found as the as the mineral tenorite (pure form is a p-type semiconductor); Other uses include correcting copper deficiencies in soil, in high temperature superconductors, as source of oxygen, in the determination of nitrogen, and as a dietary supplement; [Merck Index] Copper I oxide slowly oxidizes in moist air to Copper II oxide; [Ullmann]
Comments
Acute copper poisoning after ingestion can cause liver injury, methemoglobinemia, and hemolytic anemia. Acute renal failure may result, secondary to massive hemoglobinuria. [Goldfrank, p. 1259] May cause irritation; Harmful by ingestion; [Alfa Aesar MSDS] See "Copper."
Biomedical References
Exposure Assessment
TLV (ACGIH)
1 mg/m3, as Cu
PEL (OSHA)
1 mg/m3, as Cu
MAK
0.01 mg/m3, respirable fraction (Cu, inorganic cmpnds)
IDLH (NIOSH)
100 mg/m3, as Cu
Explanatory Notes
The Guide in the Emergency Response Guidebook is for "Environmentally hazardous substances, solid, n.o.s."
Adverse Effects
Anemia
Hemolytic anemia
Methemoglobinemia
MetHgb is secondary toxic effect
Hepatotoxin
Hepatoxic (a) from occupational exposure (secondary effect) or (b) in animal studies or in humans after ingestion
Nephrotoxin
Yes
Diseases, Processes, and Activities Linked to This Agent
Processes
Industrial Processes with risk of exposure:
- Applying Wood Preservatives
- Battery Manufacturing
- Electroplating
- Farming (Feed Additives)
- Farming (Pesticides)
- Glass Manufacturing
- Metal Extraction and Refining
- Painting (Pigments, Binders, and Biocides)
- Petroleum Production and Refining
- Semiconductor Manufacturing
- Textiles (Fiber & Fabric Manufacturing)
- Welding
Activities
Activities with risk of exposure: