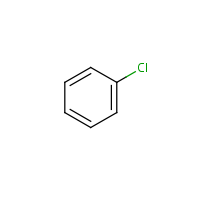
Chlorobenzene
Agent Name
Chlorobenzene
Alternative Name
Monochlorobenzene
CAS Number
108-90-7
Formula
C6-H5-Cl
Major Category
Solvents
Synonyms
Benzene chloride; Benzene, chloro-; Chloorbenzeen [Dutch]; Chlorbenzene; Chlorbenzol; Chlorobenzen [Polish]; Chlorobenzene, mono-; Chlorobenzenu [Czech]; Chlorobenzol; Clorobenzene [Italian]; CP 27; I P Carrier T 40; MCB; Monochloorbenzeen [Dutch]; Monochlorbenzene; Monochlorbenzol [German]; Monochlorobenzene; Monoclorobenzene [Italian]; Phenyl chloride; Tetrosin SP; [ChemIDplus] UN1134
Category
Chlorinated Aromatics
Description
Colorless liquid with an almond-like odor; [NIOSH]
Sources/Uses
Used as a solvent for paints, adhesives, polishes, waxes, and natural rubber; used as a dry cleaning agent and an intermediate in the synthesis of organic chemicals; [NIOSH Guidelines for Chemical Hazards] Used as a heat transfer medium, fiber swelling agent and dye carrier in textile processing, tar and grease remover, solvent for bitumen and asphalt building coatings, and pesticide solvent; [HSDB] Used in leather tanning; [PMID 21938525]
Comments
Odor threshold = 0.21 ppm; repeated or prolonged skin contact can cause burns; [NIOSH Guidelines for Chemical Hazards] In animal studies, high doses are toxic to the liver. [ACGIH] If left on clothes, can cause reddening of skin; [CHRIS] A skin and eye irritant; Ingestion can cause aspiration into the lungs; Inhalation of high concentrations can cause CNS depression; May cause kidney and liver injury; [ICSC] A mild skin irritant; Harmful by inhalation; [Alfa Aesar MSDS]
Reference Link #1
Biomedical References
Exposure Assessment
BEI
Total 4-chlorocatechol in urine = 100 mg/g creatinine at end of shift at end of workweek; Total p-chlorophenol in urine = 20 mg/g creatinine at end of shift at end of workweek;
Skin Designation (ACGIH)
Insufficient data
TLV (ACGIH)
10 ppm
PEL (OSHA)
75 ppm
MAK
5 ppm
IDLH (NIOSH)
1000 ppm
Excerpts from Documentation for IDLHs
Basis for original (SCP) IDLH: AIHA [1964] reported that 8,000 ppm was fatal to cats in 30 minutes [Patty 1963; Flury and Zernik 1931]. Patty [1963] reported that the exposure of cats for 1 hour to 2,400 to 2,900 ppm causes unsteadiness, tremor, and twitching [Flury and Zernik 1931]. Based on the data cited above, an IDLH of 2,400 ppm is chosen for this draft technical standard. . . . Basis for revised IDLH: The revised IDLH for chlorobenzene is 1,000 ppm based on acute inhalation toxicity data in animals [DeCeaurriz et al. 1981; Flury and Zernik 1931].
Vapor Pressure
12 mm Hg
Odor Threshold Low
0.08 ppm
Odor Threshold High
5.9 ppm
RD50
1054 ppm
Lethal Concentration
LC50 (rat) = 2,965 ppm
Explanatory Notes
Detection odor threshold from AIHA (mean = 1.3 ppm); Flash point = 29.2 deg C; VP from HSDB;
Half Life
Estimated from animal studies: 2 days; [TDR, p. 313]
Reference Link #2
NFPA
may ignite at ambient temp
Adverse Effects
Neurotoxin
Acute solvent syndrome
Hepatotoxin
Hepatoxic (a) from occupational exposure (secondary effect) or (b) in animal studies or in humans after ingestion
Dermatotoxin
Skin burns
ACGIH Carcinogen
Confirmed Animal
Diseases, Processes, and Activities Linked to This Agent
Diseases
Occupational diseases associated with exposure to this agent:
Processes
Industrial Processes with risk of exposure: